Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
About This Simulation
Learn the basics of Type II diabetes.
Learning Objectives
- Understand how Type II diabetes is diagnosed
- Understand the risk factors for Type II diabetes
- Understand the function of insulin in the body
- Understand how untreated diabetes affects organ function
- Regulate Type II diabetes
- Know how and when to measure blood sugar levels using a glucose meter
- Understand the effect of insulin and diabetes medication
- Prepare a syringe with insulin and know how to inject insulin
- Understand how a healthy diet and regular exercise help to regulate Type II diabetes
About This Simulation
Lab Techniques
- Blood glucose measurement
- Insulin injection
Related Standards
- HS-LS1-3
- No direct alignment
- Biology D.3 Functions of the liver
- Biology D.1 Human nutrition
Learn More About This Simulation
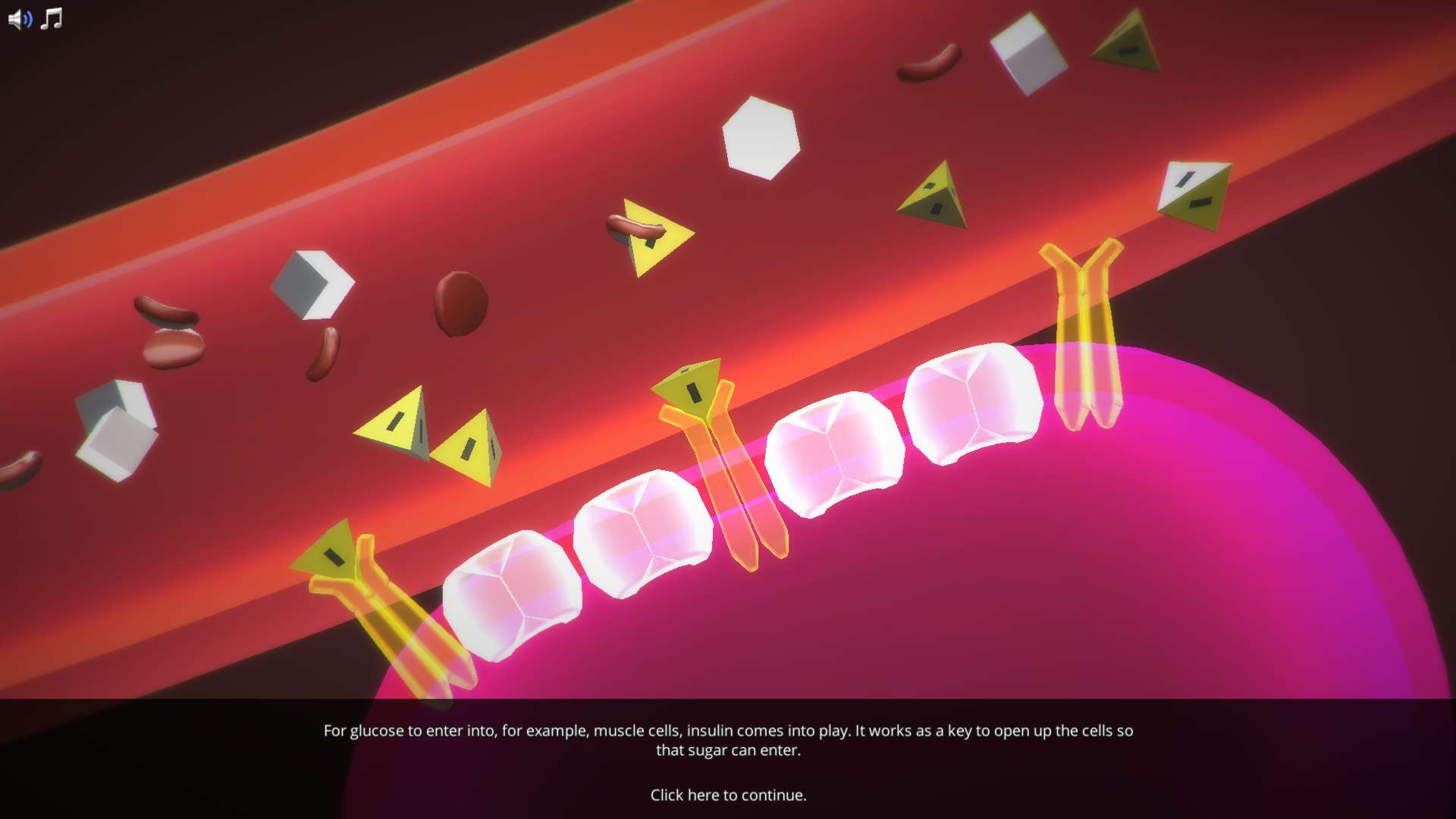
Sugar, also called glucose, is an important energy source for the human body. In order to use that energy, the body needs the hormone insulin. In diabetes mellitus, commonly referred to as diabetes, either the body does not produce enough insulin, or it doesn’t function properly. This results in a high level of glucose in the blood, which cannot be used as energy.
Two types of diabetes
We distinguish between two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. While type 1 diabetes is characterised by an early onset in children, type 2 diabetes typically develops in adults. In more detail, it can be caused by low levels of insulin production by the beta cells of the pancreas, or by reduced sensitivity of tissue cells to insulin. Both causes prevent glucose from being absorbed by cells, causing high blood sugar, also called hyperglycemia.
Learn about the consequences of type II diabetes
High blood glucose levels make it difficult for the kidneys to recover all the glucose from nascent urine, resulting in glucose being lost in urine. High glucose levels also result in less water being reabsorbed by the kidneys, causing high amounts of urine to be produced, which may result in dehydration. Over time, high blood glucose levels can cause nerve damage to the eyes and peripheral body tissues, as well as damage to the kidneys and cardiovascular system.
Apply your knowledge of diabetes
In the Diabetes lab, you will learn the basics of type II diabetes. You will learn how to measure your own blood sugar levels and even how to give yourself an insulin shot. You will also learn how to put together a healthy meal plan.
Will you be able to use your type II diabetes knowledge to manage blood sugar levels?
For Science Programs Providing a Learning Advantage
Boost STEM Pass Rates
Boost Learning with Fun
75% of students show high engagement and improved grades with Labster
Discover Simulations That Match Your Syllabus
Easily bolster your learning objectives with relevant, interactive content
Place Students in the Shoes of Real Scientists
Practice a lab procedure or visualize theory through narrative-driven scenarios


FAQs
Find answers to frequently asked questions.
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
Block quote
Ordered list
- Item 1
- Item 2
- Item 3
Unordered list
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
Bold text
Emphasis
Superscript
Subscript
A Labster virtual lab is an interactive, multimedia assignment that students access right from their computers. Many Labster virtual labs prepare students for success in college by introducing foundational knowledge using multimedia visualizations that make it easier to understand complex concepts. Other Labster virtual labs prepare learners for careers in STEM labs by giving them realistic practice on lab techniques and procedures.
Labster’s virtual lab simulations are created by scientists and designed to maximize engagement and interactivity. Unlike watching a video or reading a textbook, Labster virtual labs are interactive. To make progress, students must think critically and solve a real-world problem. We believe that learning by doing makes STEM stick.
Yes, Labster is compatible with all major LMS (Learning Management Systems) including Blackboard, Canvas, D2L, Moodle, and many others. Students can access Labster like any other assignment. If your institution does not choose an LMS integration, students will log into Labster’s Course Manager once they have an account created. Your institution will decide which is the best access method.
Labster is available for purchase by instructors, faculty, and administrators at educational institutions. You can purchase Labster by speaking with a Labster sales representative. Compare plans.
Labster supports a wide range of STEM courses at the high school, college, and university level across fields in biology, chemistry, physics, and health sciences. You can identify topics for your courses by searching our Content Catalog.